
Bladder Cancer
Each year about 10,000 people in the UK are diagnosed with bladder cancer. Men get bladder cancer much more commonly than women. It is rare for anyone under the age of 50 to get it but it becomes more common as people get older.
What are the symptoms of bladder cancer?
Passing blood in the urine (haematuria) is the most common symptom. It eventually occurs in nearly all cases of bladder cancer. In the many cases, the blood is visible during urination. In some cases, it is only detected on dipstick examination of the urine or under a microscope, and is usually discovered when analysing a urine sample as part of a routine examination.
Haematuria does not by itself confirm the presence of bladder cancer. Blood in the urine has many possible causes (see below). For example, it may result from a urinary tract infection or kidney stones rather than from cancer. It is important to note that haematuria, particularly dipstick or microscopic, might be entirely normal for some individuals. A diagnostic investigation is necessary to determine whether bladder cancer or another abnormality is present.
How is haematuria investigated?
Patients who present with significant haematuria need assessment by a urologist. Significant haematuria is defined as one episode of visible haematuria or symptomatic non-visible haematuria, or persistent asymptomatic non-visible haematuria.
A blood test will be done to measure the kidney function, and in men, after counselling, a PSA test is done.
Further tests include an ultrasound of the kidneys and bladder, or a CT scan of the abdomen and pelvis . A CT scan is the preferred method of evaluating kidney masses and is the best modality for the evaluation of urinary stones.
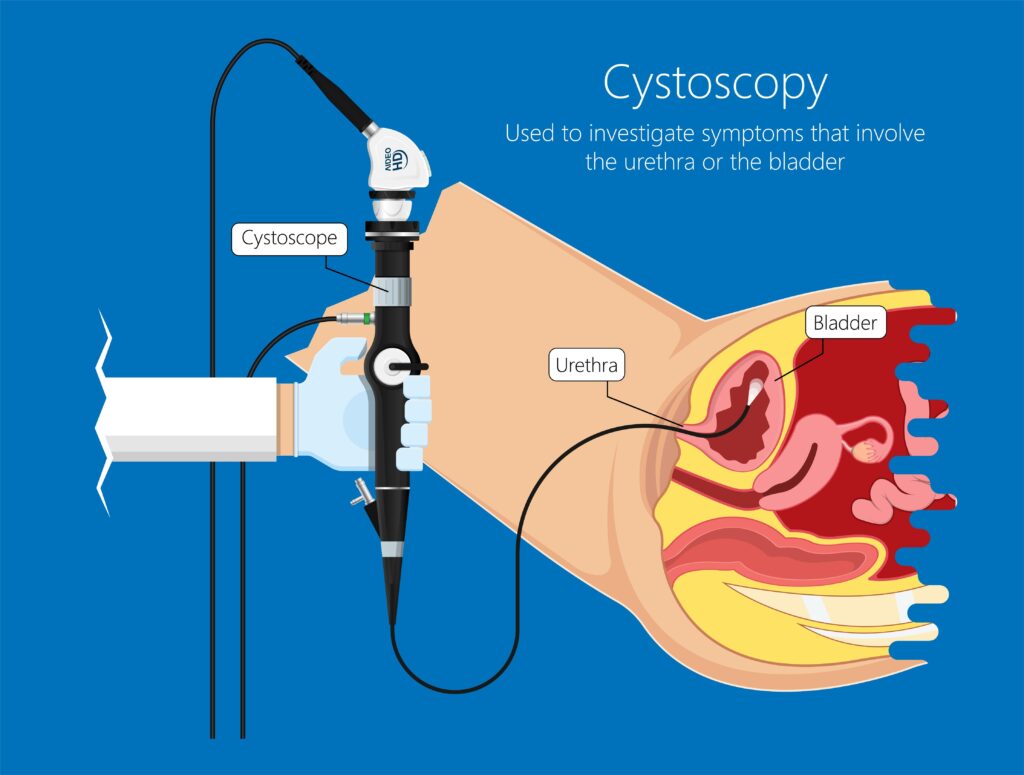
A flexible cystoscopy is ideally performed, this allows us to look into the bladder with a small flexible telescope, which is inserted via the urethra under local anaesthetic. Looking through the cystoscope your urologist can examine the inner lining of the bladder and urethra for abnormalities.
It is usually in this way that bladder cancer is diagnosed.
